Птицын С. Д., Хромова А. В. Анализ стоимости и перспектив космического туризма // Скиф. Вопросы студенческой науки. 2019. №9 (37). С. 272-276
We are at a significant historical stage, when the first success of man’s orbital flight into space has already taken place, and the near future promises us new technologies for suborbital flights. Leading modern companies are starting to compete in the spacecraft development market, which can lift to a height of more than a hundred kilometers above the ground. The last 60 years of space exploration haunted humanity. And now on the horizon there were first hopes that space tourism would become a reality not only for super-rich people, but also for the middle class.
The relevance of this work lies in the promise of space tourism. At the moment, the variety of technical means, both existing and under development, has not been fully considered. The aim of this work is to analyze the dependence of the cost of a tourist flight on the technical means used.
Methods
The work is based on the analysis of scientific papers on the subject from the database of the Samara National Research University named after Academician S.P. Queen. The following techniques were used to introduce the reader to the issue of space tourism:
1. Overview of tools for orbital and suborbital flights.
2. Carrying out a comparative analysis.
3. Coverage of the future prospects of the industry.
The relevance of this work lies in the promise of space tourism. At the moment, the variety of technical means, both existing and under development, has not been fully considered.
Results
This article gives a brief overview of space tourism, as an area of activity that has yet to reveal itself in all its glory. However, there are still a large number of problems associated with the implementation of this idea, and most importantly — with the price for the consumer. The cost of a space flight reaches $ 60 million, and the service is provided by one exclusive player in the market. Such a high price is due to the difficulty of launching the rocket beyond the Earth, the complex technological process of creating and preparing the necessary materials, as well as the high risk to human health [1]. It is easy to understand that under such conditions, space tourism is possible only for the richest people on the planet. But, as was shown in this article, there is a solution. And it is already being developed. Suborbital flights, which can deliver you to a height of 100 kilometers, will take no more than three hours and will cost much less. For 200 thousand dollars you will get the opportunity to feel like an astronaut with minimal training and a health hazard [2]. The only question remains is when the first space planes will take passengers on board.
Discussion
More than sixty years of painstaking development of the space industry have not gone unnoticed. The diverse use of satellite technologies, scientific research, the study of space and its objects: all this made possible the level of technical development that we are seeing now (Figure 1).
Towards the end of the twentieth century, more than half a dozen entrepreneurial companies struggled to get private sector funding to develop a reusable space engine. And as you can see now, many of them have achieved excellent results. Here we end a brief overview of the history of space tourism and go directly to the technologies that allow it to be implemented [3].
But as for the commercial space flights themselves? Who needs them and is it worth working in this direction? The results of a survey conducted in Southern England in 2011 speak for themselves (Figure 2). More than half of the respondents expressed their desire to fly into space. We are seeing quite a large demand in the space tourism market. And the huge revenues that this demand holds for companies.
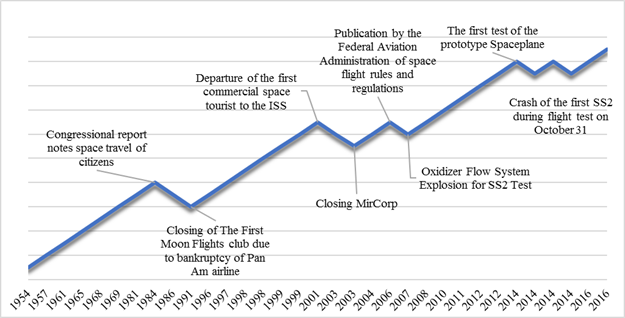
Figure 1. Stages of space tourism development
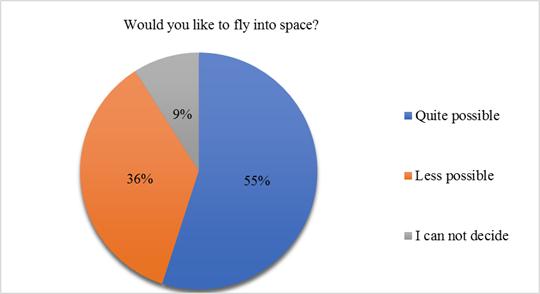
Figure 2. Southern England Survey Results
Recent data from the International Tourism Organization has shown the strong economic potential of space tourism. In 2012, the entire tourism industry was estimated at approximately 1.15 trillion dollars, in this amount only a percentage brings as much as 11.5 billion dollars annually [4]. With such an economic potential of the market, with developed technologies and production secrets, the development of space tourism will obviously attract large investments in the future. At the beginning of 1994, it was expected that the number of space tourists around the world would be about 500 thousand people per year at a ticket price of 100 thousand dollars (Figure 3). Thus, revenue would be $ 50 billion annually. With such a forecast, space tourism could reach 5% of the total tourism volume.
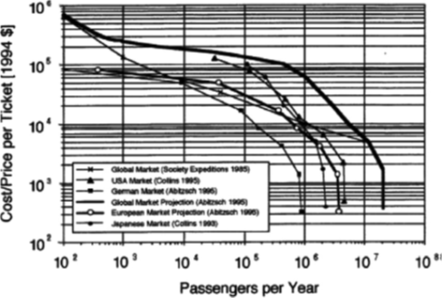
Figure 3. Number of expected passengers as a function of ticket price
Do not forget that space tourism is not the only reason for rocket launches into space, but rather the very latest. The space launch market is huge and most of it is occupied by communication satellites. The same television, navigation and more. This is followed by launches for security purposes, cargo delivery to the ISS, as well as scientific research. But why is such a promising direction occupies only a small percentage of the market? We were interested in this issue, and we decided to sort it out in detail.
The issue here is quite simple. This is a huge price that goes to launch a spaceship. For domestic hardware of the Soyuz series, it is about $ 60 million. And the costs of a tourist who wants to visit the ISS are on average $ 52 million [5]. It turns out that the tourist here act as a sponsor or investor of the entire launch. How could such a situation be? Even if we assume that such a high price is due to the cost of training, equipment, insurance and other expenses, then at least half of the cost of launch is paid at the expense of the attracted tourist. Obviously, budget financing of the space industry leaves much to be desired, therefore, other ways to obtain financial resources are being sought. Well, such an approach has a place to be, and we cannot call it unfair [6].
It is worthwhile to dwell in more detail on the means that will help the tourist reach the ISS and see the Earth from orbit. Currently, the main travel company providing such unusual services is the American Space Adventure. It works together with our Roscosmos, and all tourists over the past 10 years (seven people) have used the services of this company and the Soyuz series ships. These spacecraft are very reliable, as their modifications continue to develop for 40 years. At the moment, for the delivery of astronauts and cargoes to the ISS, only these technical means are used. As for the cost, it is from 60 million dollars as stipulated above. Such a high price is due to the high cost of labor and materials necessary to create a rocket carrier and a manned ship. Roscosmos does not provide more detailed data.
So, we are faced with the main problem of manned space flight — with the price. After all, 52 million dollars is a lot of money and few private individuals can afford to ride into orbit. In addition, there are very few spaces in ships that enter the Earth’s orbit, and only empty seats are sold for tourists, which are very rare. It turns out that with such prices on the market, servicing people a year and other nuances, it will not work to satisfy the demand on the market. Is there any other solution to this problem? We figured out the issue and, indeed, there is a solution [7].
A potential way to travel into space may be the so-called suborbital flights. Unlike orbital, a special plane will lift you to a height of about 100 km. Where you can spend 5-10 minutes. This is quite enough to feel weightlessness and enjoy the beautiful view of the Earth from space. The total travel time will be from 2 to 3 hours, after which you will return to the airport from which you took off. The price of this service is approximately 200 thousand dollars. The main difficulty is that there is still no technical means that would perform such a flight. But they are actively designed. At the moment, there are at least 4 suborbital spacecraft projects under development. The most promising of them is Lynx from XCOR. He is the only spaceship that has been accredited by the American Agency for Commercial Transportation in Space. Another interesting project is the SpaceShipTwo ship from Virgin Galactic. It has its own fuel and acceleration system, which sets it apart from its competitors. Unfortunately, one of the prototypes crashed on a test flight on October 31, 2014. At the moment, a new engine is being developed. Similar projects are Dream Chaser from SNC and SpacePlane from Airbus Defense and Space. They also have a purpose, only technologies are slightly different.
Table 1. Comparison of technical means for orbital and suborbital flights
| Subject of comparison | Suborbital flights | Orbital flights |
| Technical means | XCOR: LynxVirgin Galactic: SpaceShipTwoAirbus Defense and Space: SpaceplaneSNC: Dream Chaser | Launcher / Soyuz manned spacecraftUSA: Space Taxi (under construction) |
| Owner | Private companies | Government |
| State of the art | Low (about 10 years of development) | High (over 50 years of development) |
| Capacity, people | 1 to 6 / flight | 3 / flight |
| Flight frequency | From a few to 10 per day | 2 per year |
| Prospects | High | Low |
Such a number of developed projects cannot but rejoice. According to optimistic forecasts, the first suborbital flights may begin as early as this decade. The main advantages of suborbital technologies are:
- Price. About 200 thousand dollars. This is many times less compared to orbital flights. In the future, the price may be reduced due to competition.
- Number of flights per day. Some companies forecast up to 5-8 flights per day, thereby providing services to more people than ever before [7].
Thus, the great future of suborbital flights is becoming quite expected. Their absolute advantages give space tourism a great chance to become a full-fledged industry in the next 10-20 years. And these are thousands of satisfied customers per year and billions of dollars of profit for the entire industry. But orbital flights cannot be discounted. In the future, leading companies have plans for excursions to the moon, possibly even with a landing. And who knows how soon this will happen? We can only wait and look forward with hope.
